Private cloud vs. public cloud: What’s the best for your business?
Are you pondering whether to choose between private cloud vs. public cloud for your business? You’re not alone. With the rapid evolution of cloud computing, it’s crucial to understand the differences between public and private cloud solutions to make an informed decision that suits your organization’s needs. In this blog post, we’ll dissect the key distinctions between private and public cloud, exploring their features, advantages, and disadvantages. By the end, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to determine the best option for your business.

What is a private cloud?
Imagine having your own exclusive, on-demand infrastructure and resources tailored to your organization’s specific requirements. That’s precisely what a private cloud can offer.
Organizations that use private cloud services have the advantage of dedicated resources and enhanced security. This is in contrast to public cloud deployments, where resources are shared and managed by third-party providers.
Definition of a private cloud
A private cloud refers to a computing or cloud infrastructure and environment that is solely reserved for a single customer or organization. It provides:
- Dedicated resources
- Superior security when compared to public cloud resources
- Increased control and customization
- Scalability
- Security, allowing organizations to tailor the cloud environment to suit their specific needs and requirements.
Organizations can leverage the adaptability and scalability of the private cloud model, while ensuring maintenance.
Features
Private cloud primarily features:
- Dedicated resources: resources exclusively assigned to a single user or organization and not shared with any other user or organization
- Adaptable infrastructure: infrastructure that can be easily customized and scaled to meet specific needs
- Enhanced security: increased security measures to protect cloud data privacy
Customizable infrastructure means the ability to tailor the cloud environment to meet the requirements of the user or organization, encompassing hardware, operating system, and software selection.
Enhanced security ensures data protection through encryption, authentication, and other security measures regulating access to the cloud environment.
Advantages of using a private cloud
Employing a private cloud provides numerous advantages, including heightened control, customization, and security, with greater control over data governance and data locality, more flexibility, and more scalability compared to public clouds. Private clouds provide improved privacy due to enterprise authentication and enable organizations to have their exclusive, on-demand infrastructure and resources, allowing them to tailor the environment to meet their specific requirements while maintaining a higher level of security compared to public cloud services.
Disadvantages of using a private cloud
On the flip side, private cloud can come with some drawbacks, such as:
- Increased expenses
- The need for internal expertise
- Maintaining your hosting infrastructure and managing resources can lead to higher costs and more intricate management compared to public cloud services.
Use cases of private cloud
Private cloud is particularly beneficial for organizations that have strict security and compliance requirements, especially those handling confidential and sensitive data and prioritizing privacy. Examples of sectors that would likely benefit from a private cloud include government and healthcare organizations, where data protection is paramount.
What is a public cloud?
Unlike the exclusivity of a private cloud computing resources, a public cloud refers to a cloud computing environment where a third-party provider owns and manages shared resources for multiple users. Managed public cloud providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) offer scalable, flexible, and cost-effective solutions to a wide range of organizations, delivering their services over the Internet or through dedicated connections, using a pay-per-use approach.
Providers often offer a wide range of services, or Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), from basic compute and storage to more complex services such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, with a range of tools and services to help customers.
Definition of a public cloud
A public cloud represents a cloud deployment model where a public cloud provider owns and operates cloud computing services on premises infrastructure, making computing resources accessible to multiple tenants over the Internet.
Public cloud offers:
- Scalability
- Flexibility
- Cost savings
- Managed by the provider, allowing users to access it from any location with an internet connection.
The advantages of public cloud include the ability to quickly scale up or down to meet changing demands, often relying on a data center infrastructure for optimal performance.
Features
The features of a public cloud include:
- Scalability: allows businesses to effortlessly adjust resources as needed
- Pay-as-you-go pricing: Organizations are charged only for the resources they utilize
- Shared infrastructure: Multiple organizations share the same physical hardware and resources
Shared infrastructure enables multiple customers to access the same resources, maximizing cost efficiency.
Advantages of using a public cloud
The benefit of using a public cloud is primarily:
- Cost savings
- Flexibility
- Straightforward deployment
- Scalability
- Simplified disaster recovery
- Staying up-to-date
- Resource availability
Moreover, public cloud users don’t have to worry about managing the public cloud computing resources themselves, as the cloud service provider typically manages the public cloud infrastructure.
Disadvantages of using a public cloud
Despite its advantages, public cloud does have some limitations, including potential security issues and restricted customization. As public clouds are shared environments, users must be aware of the potential risks associated with sharing resources with other tenants.
Although public clouds are typically more secure, they may not offer the same level of control and customization as private clouds to satisfy specific security requirements.
Use cases of public cloud
Organizations with unpredictable workloads and less rigid security requirements would find the public cloud ideal. Use cases for the public cloud include:
- Web hosting
- Disaster recovery
- Web development and QA testing
- Short-term projects
- Global web applications
- Various data-related tasks such as databases, messaging, ETL, data translation, middleware, big data, and artificial intelligence.
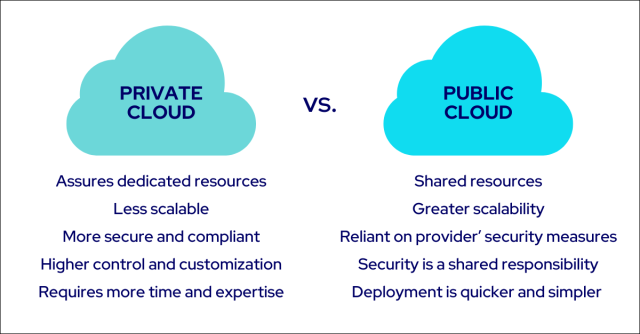
Private cloud vs. public cloud: Analyzing the key differences
Now that we’ve explored private and public cloud, let’s compare the two, focusing on infrastructure, security, and deployment.
Infrastructure: Private cloud offers more control over the hardware and software used, while public cloud offers more control over hardware and software.
Infrastructure and scalability
While private cloud infrastructure assures dedicated resources, public cloud infrastructure presents scalable and shared resources.
Private cloud is generally less scalable than public cloud infrastructure due to its resource limitations, while public cloud infrastructure can access a wider range of resources, offering greater scalability.
Security and compliance
When it comes to security:
- Private cloud is more secure and compliant
- Public cloud security is a shared responsibility between the provider and the user
- Private cloud offers a higher degree of control and customization to meet specific security requirements
- Public cloud security depends on the shared infrastructure and the provider’s security measures
Deployment and management
Private cloud deployment requires more time and expertise, as it involves advanced coding and engineering knowledge, in addition to a substantial initial investment in infrastructure and personnel.
On the other hand, public cloud deployment is quicker and simpler, as the provider assumes the costs of hardware and software and manages the infrastructure.
How to assess the right cloud option for your business
So, how do you decide which cloud option is right for your business? Consider factors such as:
- Business needs
- Security requirements
- Cost
Factors to consider
Factors such as scalability, security, and cost should be considered when choosing between private and public cloud. Private clouds usually necessitate a substantial initial investment yet can provide more cost savings in the long run, while public clouds are usually more economical in the short term but may not provide the same level of cost savings over time.
It is important to weigh the pros and cons of each option carefully before making a decision.
Your business needs
The choice between public cloud vs. private cloud environments should be guided by the needs of your business. Private cloud is more suitable for organizations with strict security and compliance requirements, as it offers greater control and flexibility, enabling organizations to customize their cloud environment to meet their exact security and compliance requirements.
Organizations that require a high level of security and compliance can benefit from the control and flexibility of the organization.
Security and safety requirements
When deciding between private and public cloud providers, security and safety requirements should be taken into account. Private cloud offers superior security.
Some key security and safety requirements to consider are:
- Data encryption
- Access control
- Data backup and recovery
- Compliance and certifications
- Physical security
- Incident response and monitoring
- Service level agreements (SLAs)
- Vendor reputation and reliability
Cost
Undeniably, cost plays a significant role in choosing between private and public cloud providers. Public cloud is generally more cost-effective than a private cloud, as the cloud provider assumes the costs of hardware and software.
However, the expense of operating a private cloud is contingent upon the magnitude and complexity of the private cloud resources and infrastructure, in addition to the cost of the hardware and software employed.
Hosted private cloud—A game changer
If you remain undecided, a hosted private cloud is a game changer that may be worth considering. It merges the benefits of a private cloud, like dedicated resources and superior security, with the scalability and cost efficiency of a public cloud.
Hosted private clouds provide the best of both worlds, allowing private cloud users to customize their private cloud environment vs. private cloud solutions with less flexibility.
Features and benefits
A hosted private cloud combines benefits from both private and public cloud, including dedicated resources, enhanced security, scalability, and cost-efficiency.
This allows organizations to enjoy the best of both worlds, meeting their unique requirements while capitalizing on the advantages of cloud computing.
Perfect for businesses and organizations
Businesses and organizations that need the control and security of a private cloud but desire the flexibility and cost-effectiveness of a public cloud would find hosted private cloud ideal. With hosted private cloud solutions like Flexential, organizations can leverage a comprehensive and flexible approach to building hybrid cloud solutions, combining the best of both private and public cloud environments.
Flexential Hosted Private Cloud
Flexential Hosted Private Cloud provides a comprehensive and adaptable approach to developing hybrid cloud solutions, integrating the benefits of both private and public cloud environments. With Flexential innovative solutions, businesses can enjoy the following benefits:
- Enhanced security
- Control
- Customization
- Cost savings
- Scalability
By leveraging the power of both private and public cloud environments, Flexential helps manage complex hybrid infrastructure to create a secure and flexible environment tailored to your business.
Summary
In conclusion, the choice between private and public cloud depends on your organization’s specific needs and requirements. Private cloud offers dedicated resources, enhanced security, and control, while public cloud provides scalability, cost savings, and ease of deployment. Hosted private cloud solutions, like Flexential, can be the perfect middle ground for businesses seeking the best of both worlds. By understanding the key differences and considering your business needs, you’ll be able to make a well-informed decision and harness the power of the cloud to propel your organization forward.